Understanding some of the most prevalent mental health disorders is crucial for anyone looking to support individuals with these conditions. Here, we will outline several key types of disorders and provide an overview of their symptoms and potential impact on individuals’ lives.
Mood Disorders
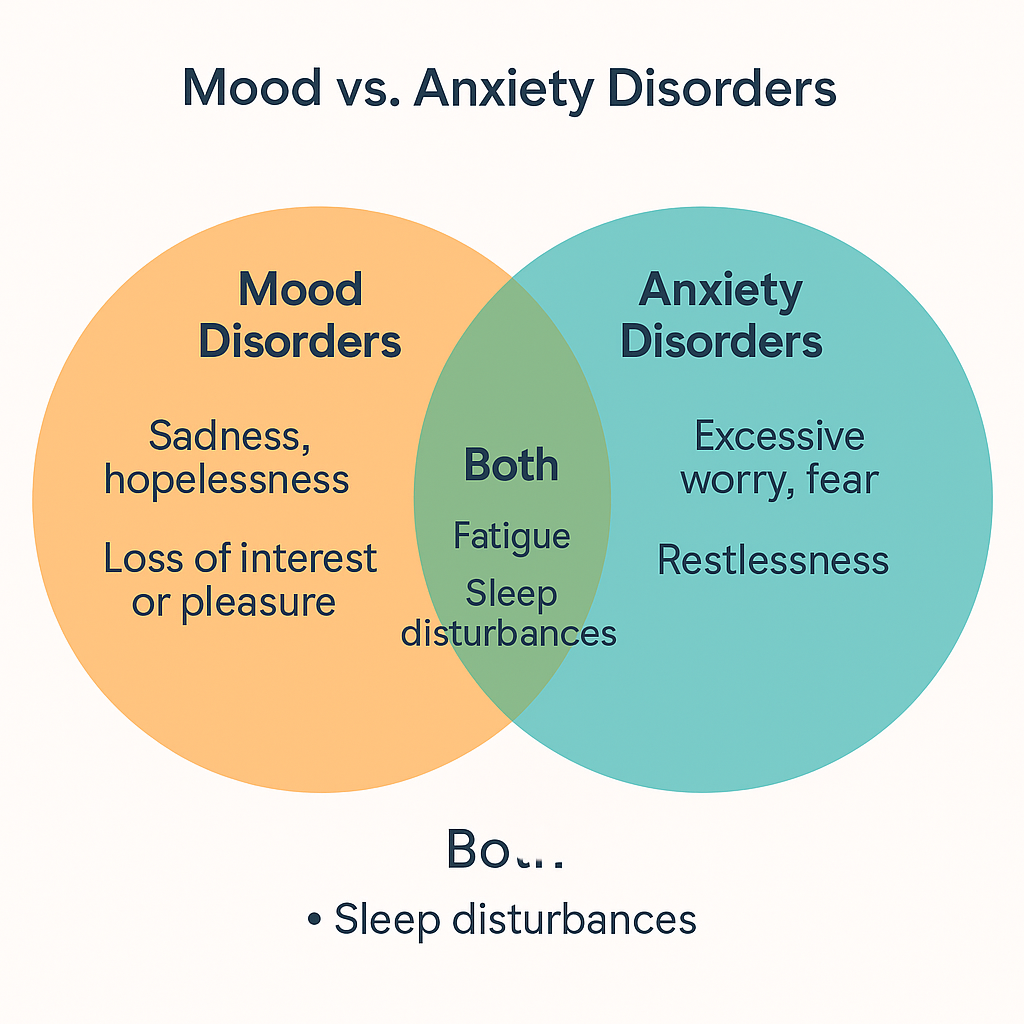
Mood disorders primarily affect an individual’s emotional state. The most common among these are depression and bipolar disorder. Depression is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest or pleasure in activities. Bipolar disorder involves extreme mood swings, ranging from depressive lows to manic highs, which may include increased energy, reduced need for sleep, and heightened impulsivity.
Anxiety Disorders
These disorders are marked by excessive fear or worry that can interfere with daily activities. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), Panic Disorder, and Social Anxiety Disorder are widespread types of anxiety disorders. GAD is characterized by chronic, exaggerated worry about everyday life, while Panic Disorder involves sudden and intense episodes of fear or discomfort, known as panic attacks. Social Anxiety Disorder entails a significant fear of social situations due to concerns about being judged or embarrassed.
Psychotic Disorders
Psychotic disorders involve distorted thinking and awareness, including delusions (false beliefs) and hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that aren’t there). Schizophrenia is one of the most recognized psychotic disorders, which can cause significant challenges in thinking clearly, managing emotions, making decisions, and relating to others.
Personality Disorders
These disorders are characterized by enduring patterns of behaviour, thinking, and feeling that deviate markedly from the expectations of the individual’s culture. Examples include Borderline Personality Disorder, which involves instability in moods, self-image, and behaviour, and Antisocial Personality Disorder, which is associated with a disregard for social norms and the rights of others.
Eating Disorders
Eating disorders involve preoccupations with food, weight, and body shape, leading to harmful eating behaviours. Anorexia Nervosa, Bulimia Nervosa, and Binge-Eating Disorder are among the most common types. Anorexia Nervosa is characterized by a distorted body image and an extreme fear of gaining weight, resulting in severe food restriction. Bulimia Nervosa includes episodes of binge eating followed by compensatory behaviours such as vomiting, while Binge-Eating Disorder involves recurrent episodes of eating large quantities of food without subsequent purging behaviours.
Substance-Related and Addictive Disorders
These disorders involve the misuse of substances like alcohol, drugs, and tobacco, which can lead to significant impairment or distress. Addiction can result in a range of harmful physical, psychological, and social consequences.
