To address the impacts of climate change on biodiversity, adaptation and mitigation strategies are essential:
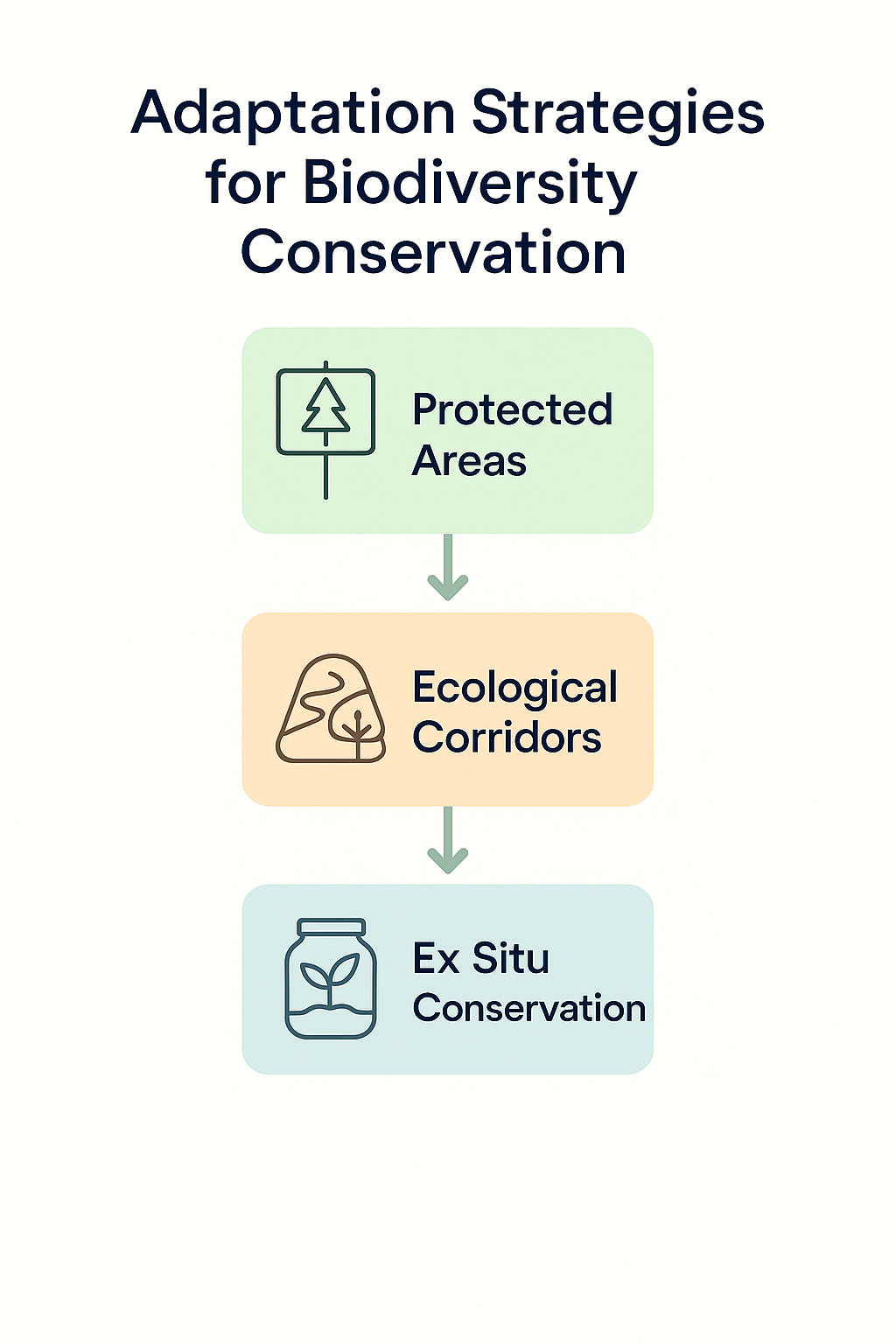
– Protected areas: Establishing and managing protected areas can conserve important habitats and provide refuges for species.
– Ecological corridors: Creating corridors between protected areas can facilitate species migration and genetic exchange.
– Assisted migration: In some cases, species may be relocated to more suitable habitats.
– Ex situ conservation: Conservation of species outside their natural habitats, such as in seed banks or botanical gardens, can safeguard genetic diversity.
– Mitigation efforts: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions can slow the rate of climate change and decrease its impacts on biodiversity.
Community involvement is crucial in implementing these strategies. Local knowledge and engagement can enhance the effectiveness of conservation efforts and ensure that they are culturally appropriate and sustainable.
